A thermally-stressed LED light quickly loses efficiency and has diminished lumens-per-watt output, affecting its brightness. If LED thermal management is unable to meet the temperature specifications of the LED, a breakdown, or other undesirable effects – such as internal solder-joint detachment, damage to die-bond epoxy or lens yellowing – may occur.
For this reason, many LED applications require high-performance heat sinks capable of removing heat from the LEDs. Aluminum heat sinks manufactured by a liquid-forging process offer a number of heat-transfer advantages in comparison to products manufactured by competing techniques.
Why Liquid Forging?
Liquid Forging is an innovative metal-forming process, developed by the Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology (SIMTech), which allows complex geometries with pore-free parts to be produced with minimal material wastes. This process harnesses wrought aluminum alloy to create a liquid melt, which can be easily fashioned into a comprehensive range of products that allows for flexibility in design.
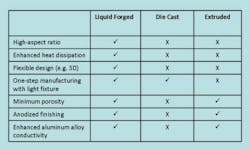
Some advantages of liquid-forged heat sinks relative to other conventional processes include:
Improved thermal performance
Liquid-forged heat sinks offer improved thermal performance i a variety of ways:
- Aluminum-wrought alloys conduct heat faster than cast alloys used in die casting. Also by incorporating a copper base, the heat sink achieves 4 times better thermal conductivity.
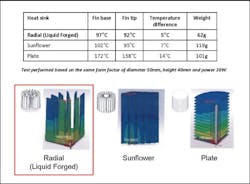
- Intricate fins and pins deliver a higher aspect ratio, increasing the surface area for ambient heat transfer. With no centre core, heat removal by convection is also improved compared to heat sinks made by conventional processes.
- Porous-free microstructure eliminates air pockets for rapid, continuous heat transfer through the heat sink to the surroundings.
- Anodized heat sinks can further improve thermal performance by an additional 10-15%.