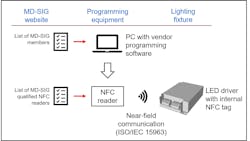
Manufacturers of LED luminaires currently use a variety of programming methods to set the operating characteristics of LED drivers inside luminaires. Simplified and harmonized methods are desired to enable LED driver programming on automated or manual production lines.
Members of MD-SIG, a lighting-industry consortium, have successfully standardized a digital, wireless programming approach using near-field communication (NFC).
NFC allows the manufacturer to wirelessly set the LED driver operating parameters, such as operating current, constant lumen output and dimming levels. This can be done on a manufacturing line without the need to apply mains voltage to the driver.
MD-SIG members include leading global vendors of LED drivers, and some of these companies have already implemented different approaches to NFC programming. Now, these companies have agreed to harmonize their programming methods, and will use the ISO/IEC 15963 standard for NFC.
NFC programming is faster than traditional methods of LED driver programming, more feature-rich and flexible than resistor-setting techniques, and has a reduced training requirement for production-line staff. This technology could also offer new in-field services in the future e.g. installation and maintenance of street-lighting luminaires.
The NFC system uses a programming device, commonly known as an NFC reader, which wirelessly transfers the programming data to an NFC tag inside the LED driver. The parameters are programmed using a standardized NFC reader in combination with software that is specific to the LED driver vendor. A list of qualified NFC readers is available on the MD-SIG website.
MD-SIG compliant equipment and software enables luminaire makers to streamline their production and to use LED drivers from different vendors using the same programming hardware.
Members of MD-SIG have access to the NFC programming specification, which describes the system setup and the requirements that are mandatory to achieve compliance of the programming software, the NFC reader, and the LED drivers and other luminaire components.
“Harmonization of NFC programming methods will help to simplify the mass programming of LED drivers in production environments,” says Arnulf Rupp, Chair of MD-SIG. “Luminaire makers can now use a single MD-SIG compliant NFC reader in combination with vendor-specific software packages. This allows luminaire makers to easily use LED drivers from different vendors as required.”
MD-SIG is an open organization, and all interested parties are invited to join us in order to access our specifications and contribute to our ongoing work.
About MD-SIG
The Module-Driver Interface Special Interest Group (MD-SIG) is a global lighting-industry consortium, and aims to meet the growing demand in the market for harmonization by introducing a standardized, multi-vendor electrical interface for LED drivers and LED modules.
MD-SIG is harmonizing existing setting methods and power-interface definitions for LED drivers, and introducing new setting and programming methods. The consortium has already released specifications for critical definitions and for an analogue method of current setting, and has now added a specification for digital NFC programming.
For more information, please visit the MD-SIG website: md-sig.org